IDA (Interdigitated Array) Electrode
Introducing IDA (Interdigitated Array) electrode developed by NTT Life Environment Research Laboratory. Some papers about determination of micro-substance and observation of its electrochemical behavior using IDA microelectrode have been reported. This microelectrodes made using risograph technology to form micro pattern upon insulator's plate. Figure below show the structure of IDA electrode. Number of finger in one electrodes is 65 pairs. Each electrode works as oxidation or reduction electrode.
&refx(): File not found: "ida_electrode.jpg" at dir "xdata/";
= a 200x magnified image =>
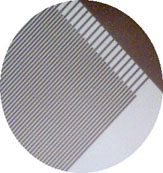
Characteristic: High sensitivity CV measurement Very small quantity electrochemical measurement Small and integrated Fast response Conductivity measurement
Applications: Electrode for liquid chromatography Electrode for electrochemical analysis Biosensor and chemical sensor Chemically modified electrode Electrode for Chemical reaction process control
| Catalog No. | Name | Wide(µm) | interval(µm) | length(mm) | Number of feet |
| 012125 | IDA Electrode Au | 10 | 5 | 2 | 65 |
| 011065 | IDA Electrode Pt | 10 | 5 | 2 | 65 |
| 012127 | IDA Electrode C | 10 | 5 | 2 | 65 |
| 011872 | IDA Electrode ITO | 10 | 5 | 2 | 65 |
CV measurement using Interdigitated Array Electrodes
IDA Electrode is a pair of band electrode combined and meshes with each other as a generator electrode and collector electrode, therefore it is possible to make an electrochemical redox cycle upon the electrode as showed in figure.
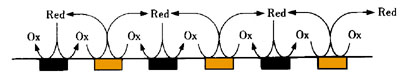
By occurring the redox cycle on electrode increasing electrolysis current to raise measurement sensitivity. In experiment using common electrodes to analyze a small quantity of sample solution, the sample will consumed and exhausted due to electrolysis. However using this Interdigitated array electrode, the oxidation-reduction reaction occur repeatedly so the sample solution will not exhausted.
Figure show Voltammogram of 10µL(a)(c) and 0.2µL(b)(d) Ferrocene sample dropped on IDA electrode. The difference between dual mode (a)(b) using both electrode to perform redox cycle and single mode (c)(d) which only one reaction (oxidation or reduction) occur at time can be found clearly. In dual mode (a)(b), the increase of oxidation current on generator electrode will followed by increasing of reduction current on collector electrodes. In (d), response become very small because consumption of object substance due to electrolysis.
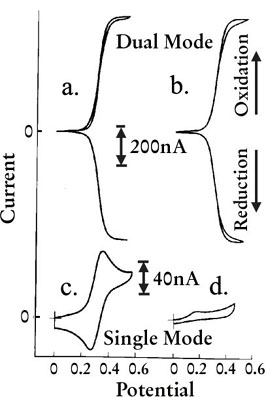
CV measurement result of solution sample using IDA electrode dual mode and single mode measurement

