Variety, Features and Shapes of Working electrodes
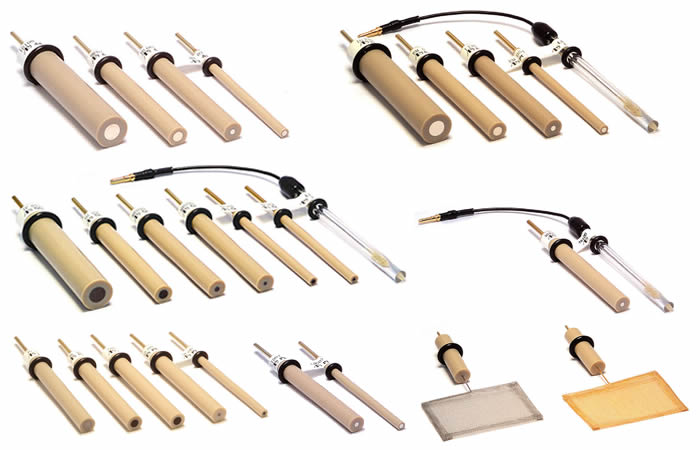

| Variety of Working Electrodes | Features and Applications |
| Platinum electrode (PTE) |
Conventional electrode, which has hydrogen adsorptive wave, used for H2O2 and oxides detection |
| Gold electrode (AUE) |
Conventional electrode, which has no hydrogen adsorption wave, used for thiols detection |
| Glassy carbon electrode (GCE) |
Chemically stable electrode despite its relatively large over-potentials of oxygen and hydrogen evolutions |
| Silver electrode (AGE) |
For cyanide and sulfide detection |
| Carbon paste electrode (CPE) |
Mixed with enzyme etc. to make modified electrodes |
| Nickel electrode (NIE) |
Chemically modified to detect amino acids |
| Palladium electrode (PDE) |
Used to study the process of adsorption and desorption of hydrogen |
| Plastic formed carbon electrode (PFCE) |
Its highly-oriented graphite edge is exposed to the surface with cost effective, similar feature of HOPG |
- Working Electrodes for Electrochemical Measurements
- Potential Window of Pt‚ Hg‚ Carbon electrodes in aqueous solution
- What is CV (Cyclic Voltammetry) Measurement?
- Working electrode selection
- Micro electrodes
Our electrodes used for electrochemical measurements such as CV,
LSV , DPV and so on are compact and easy enough to be polished by yourself.
Remove the cap covering the electrode, and check its surface prior to the first use.
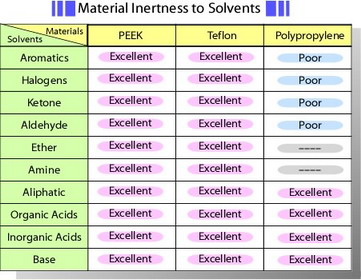
Carbon paste electrode is available in the form of carbon paste which user packs into a shallow well in the electrode holder supplied by us. Other electrodes are polished to immediate use. These electrodes are encapsulated in PEEK* - solid, well inert against solvent. Table of material inertness to solvents is shown below. However, long-term immersion in tetrahydrofuran or using under higher temperature which exceeds the temperature coefficient between plastic and electrode material might be a cause of crack. O-ring enables a position of an electrode to be adjusted in the voltammetry cell.
Akira Fujishima, Toru Inoue, Method of Electrochemical measurement, Gihodo Publishers, 1984.
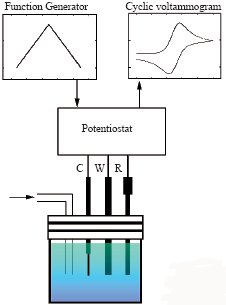
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a reversible LSV measurement which scans electric potential turned to reverse direction after reaching final potential and scan back to initial potential. In CV, the reversibility of the product produced in forward scanning can be analyzed by backward scanning. Because of this characteristic, CV has been applied widely. If a CV conducts with potential wave form as shown in right, then we can study the substance characteristic as:
- Stability in oxidized and reduced forms
- Molecular adsorption in redox process
- Measurements of kinetic rate constants
- Study of reaction mechanism
- Reversibility of electrochemical reaction
- Standard redox potential, Eo=(Epa+Epc)/2
- Electron transfer number, ΔE=Epa-Epc= 58/n
*n: electron transfer number per mole
David K.Gosser,Jr.,Cyclic Voltammetry Reaction
Mechanisms,VCH Publishers,Inc. 1994.
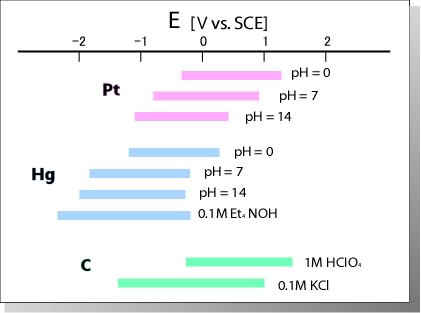
Redox potential of molecule under research have to fall in the potential window over which the background current due to the electrode itself must not disturb the experiment.
Pt (Platinum) and Au (Gold) electrodes - applied to organic or inorganic substances measurement because they have high overpotential for oxygen evolution and low overpotential for hydrogen evolution.
Hg (Mercury) electrode - well suited to measure reduction of metal ions because of its high overpotential for hydrogen evolution. Hg electrode can easily observe the reduction of Zn.
At the measurement with non-aqueous solvent, hydrogen/oxygen overpotential does not affect. Instead of that, decomposition potential of the non-aqueous solvent and supporting electrolyte comes to an important factor. Furthermore, impurity of water in non-aqueous solvent makes the potential window narrower depending on the quantity of the water.
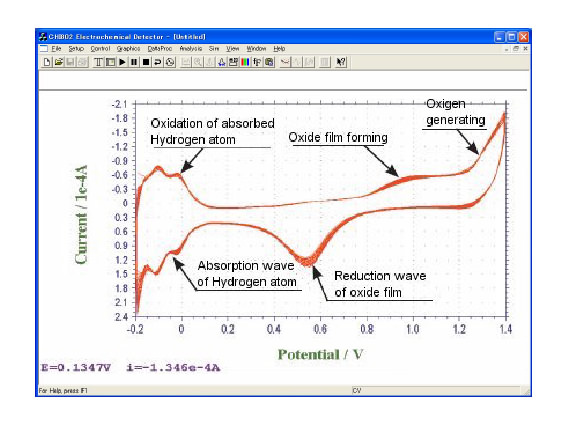
Figure: Current-Potential curbs of the result of 50 times scanning by immersing a Pt electrode in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. Reiteration of the cycle obviously activates the electrode. Although there is absorption wave at the cathode side, it is possible to observe other reaction of the electrodes in this potential range because this reaction requires only certain quantity of electricity.
Advantages of Microelectrodes use for CV measurement
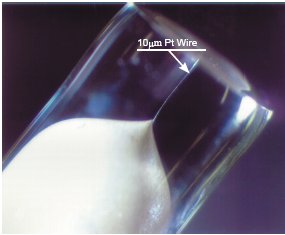
| 1. Little distortion from dissipation in potential or electrification flow 2. Combination of PC enables to process at high sweep rate 3. Analyzable short-lived intermediate in electrode reaction 4. Mearsurable without support electrolyte 5. Excellent measuring accuracy because of little influence of noise arising from electrification flow 6. Smooth diffusion enough to obtain stationary state |
vsAg_Ag_plus.jpg) |
Figure in right : the result of detection of a chemical product in subsequent reaction. By the faster sweep at 104 V/S, the peak (which is shown when the short-lived intermediate is reduced into the former substance) can be observed before the intermediate vanishes. Kosuke Izutsu, Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions, WILEY-VCH, 2002. |

