TOP > Technical note > Experimental data on RHEK
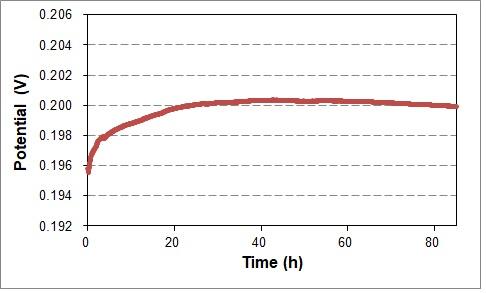
RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode potential change over time
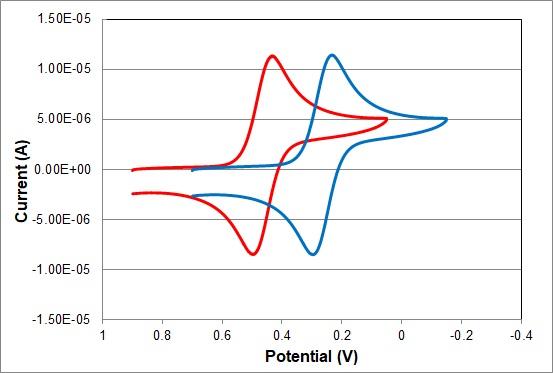
Red line: RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode Blue line: RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl)
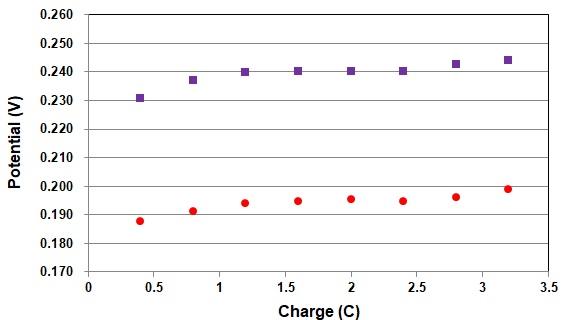
Purple■:RE-2BP Calomel Reference electrode Blue●:RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl)
Experimental data on RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode
RHE (Reversible hydrogen electrode) was tested for the evaluation, where the stability of the potential in function of the time and temperature was tested and compared with the reference against SHE. Also, the potential difference between RHE and line up reference electrode was measured.
- Time series change of the potential
- Comparison of Cyclic Voltammograms between RHE and Ag/AgCl reference electrode
- Potential difference between RHE electrode and others reference electrodes changing hydrogen level
Time series change of the potential
| Experimental conditions | |
| Reference electrode: | RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode |
| Working electrode: | RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl) (Cat. No. 013503) |
| EC technique: | open circuit potential - time |
| Solution: | 1.2 mol/L Hydrochloric acid solution |
| Charge passed for hydrogen generation: | 2 C |
| Temperature: | 25°C |

RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode potential change over time
RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl) (Cat. No. 013503) was connected to the potentiostat working electrode connector.
The potential change after 80 hours of electrolysis was about 5 mV, and about 1 mV from 20 to 60 hours.
The potential change after 80 hours of electrolysis was about 5 mV, and about 1 mV from 20 to 60 hours.
Comparison of Cyclic Voltammograms between RHEK and Ag/AgCl reference electrode
| Experimental conditions | |
| Reference Electrode: | RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode with Double junction chamber and 1.2 mol/L Hydrochloric acid solution |
| RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl) (Cat. No. 013503) | |
| Working Electrode: | PTE Platinum electrode OD: 6.0 mm ID: 1.6 mm (Cat. No. 002013) |
| Counter Electrode: | Platinum counter electrode 23 cm (Cat. No. 012961) |
| EC technique: | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| Applied Potential: | 0.9 V ∼ 0.05 V (RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode), 0.7 V ∼ -0.15 V (RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl)) |
| Scan Rate: | 0.1 V/s |
| Solution: | 2 mmol/L K3Fe(CN)6 + 1 mol/L KNO3 |
| Temperature: | 25°C |

Red line: RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode Blue line: RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl)
The difference between the peak potentials of the two cyclic voltammograms is 0.201 V, which is approximately equal to the potential 0.198 V of the saturated KCl silver-silver chloride reference electrode for the standard hydrogen electrode at 25°C.
Comparison of the potential difference between RHE electrode and others reference electrodes changing hydrogen level
| Experimental conditions | |
| Reference Electrode: | RHE Reversible hydrogen electrode |
| Working Electrode: | RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl) (Cat. No. 013503) |
| RE-2BP Calomel Reference electrode (Cat. No. 013458) | |
| Counter Electrode: | Platinum counter electrode 23 cm (Cat. No. 012961) |
| EC technique: | open circuit potential - time |
| Solution: | 1.2 mol/L Hydrochloric acid solution |
| Temperature: | 25°C |

Purple■:RE-2BP Calomel Reference electrode Blue●:RE-1CP Reference electrode (Ag/AgCl/Saturated KCl)
When 1.2 mol/L hydrochloric acid is used in the electrolytic solution at 25°C, it is found that the potential of each reference electrode is almost stabilized when the amount of electric charge during electrolysis exceeds 1 C.

