Part 12: Amperometry technique (i-t)
These are chronoamperometric techniques. That is, current is measured as a function of time. Typically, such techniques are used for current titration, amperometric sensors, flow cells, etc.
The difference between the three available techniques is the potential waveform used. That is, the potential waveform is devised to improve selectivity. The simplest potential waveform is the fixed potential. This is a TB waveform. The shape of the TB and a typical current response are shown in Fig.12-1 and 12-2, respectively.
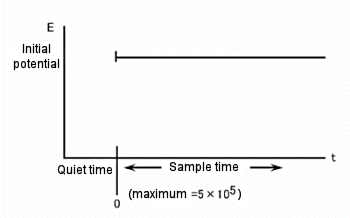
Fig. 12-1 Potential waveform of TB.
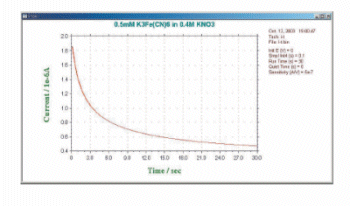
Fig. 12-2 Typical current response of TB.
One variant of the amperometric potential waveform superimposes a continuous pulse of constant amplitude (Fig. 12-3). This is a differential pulse amperometry (DPA) technique that involves cleaning the electrodes. The current is sampled just before the pulse and before the end of the pulse, allowing for effective elimination of background currents. Since the differential current is displayed, this method allows the potential window to be checked and helps improve detection selectivity. A typical current response of a DPA is shown in Fig. 12-4.
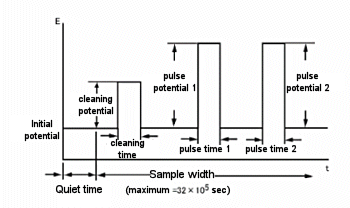
Fig. 12-3 DPA potential waveform.
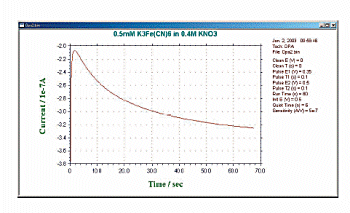
Fig. 12-4 Typical current response of DPA.

