Part 19: Impedance-Potential (IMPE)
The impedance-potential method increments potential E from the initial potential to the final potential. A continuous sine wave is superimposed on the base potential. Current and voltage are sampled and analyzed for real and imaginary impedance components. The impedance is recorded as a function of potential. The following figure shows the applied potential waveform as a function of time.
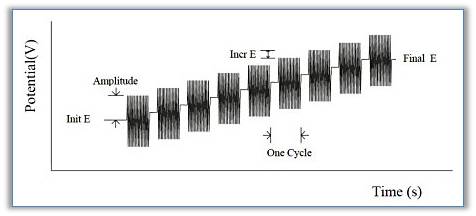
Fig. 19-1 Impedance-Potential waveform.
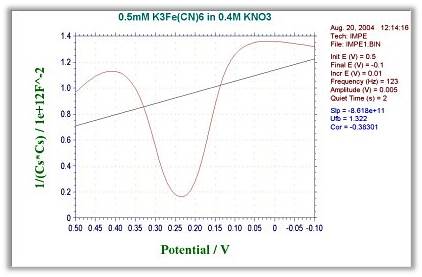
Fig. 19-2 Mott-schottky plot.
-Types of data that can be plotted
- LogZ - E
- phase - E
- Z - E
- Z' - E
- Z" - E
- log(Z" & Z') - E
- logY - E
- Y - E
- Y' - E
- Y" - E
- log(Y' & Y") - E
- Rs - E
- Os - E
- Rp - E
- Cp - E
- 1/(Cs*Cs) - E : Mott-schottky
- 1/(Cp*Cp) - E : Mott-schottky

